Post Windows 2000 and Windows XP, the use of the Windows Command prompt has been on the decline. Everything that is done on Windows today is done through the graphical user interface. There are still some tasks that are done through the Command prompt, but we aren’t going to discuss about commands available for the Command line. There are plenty of references for that. Rather, we are going to find out those tricks that make working on the prompt easier.
1. Copy and Paste Text
If you have ever tried to copy and paste stuff into the command prompt window, you must have discovered that Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V doesn’t work. You can however copy text from other applications, right click on the command prompt windows and click Paste. But how do you copy text from the command prompt? There is a strange way to do it.
First right-click inside the command prompt window and click on Mark. The title bar of the window should read Mark Command Prompt.
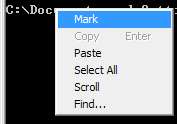
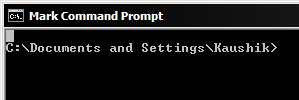
Now drag a box around the text you want to copy. The selected text will get highlighted.
Right-click again to automatically copy the selected text into the clipboard. Now again right click and choose the paste option to paste the text. You can also paste this text into other Windows applications.
There is an easier way to copy paste text in command prompt.
Right-click on the title bar and click Properties. Under the Options tab check the box for QuickEdit Mode.

Now you can straightaway drag and select text you want to copy, right-click to copy the text to the clipboard and right-click once again to paste it at the desired location. No need to go into the context menu to choose Paste. This option can be enabled either for the current command prompt window or for all instances of command prompt.
2. Command Prompt History
Do you know that command prompt has a history? Simply press F7 to display the list of commands entered during the current session. Use the arrow keys to select and command from the list you want to run.
To run the previously entered command press F3. To run any command from the history list by it’s number, press F9 and type the command number.
3. Drag and drop to enter file path
There are two ways to execute applications using the command line – 1) navigate into the directory where the application resides using the CD command and then type the application name, or 2) type the full path of the application from any location. Either way, it involves lot of typing particularly if the application is inside directories several levels deep.
The easiest way to avoid typing the path name is to simply drag the applications icon into the command window and release it to automatically enter the path of the application. Now you just have to press Enter to run it. You can also drag folders into the command prompt window.
4. AutoComplete
To help you with entering commands and file paths, the command prompt also has an auto complete feature which allows you to complete filenames without typing the entire name. Type the first few characters and click TAB to cycle through all available filenames and folders.
5. Full Screen Mode
In the days of DOS, the command window ran full screen. But from Windows 2000 it started running inside a window. If you prefer to run it full screen, press ALT+ENTER to go into full screen mode. Use the same shortcut to exit full screen. Notice that Windows Media Player uses the same shortcut for running full screen, so this should be easy to remember.
6. Customize the look of the command prompt
If you are tired of the black screen, you can make a few changes to make it look livelier. All customization options are available by right-clicking on the title bar and clicking Properties. Change cursor size, window size, fonts, colors and more.

Comments
Post a Comment